Insurance is an essential aspect of managing risk and protecting oneself from potential financial loss. When obtaining an insurance policy, understanding the various terms associated with it becomes crucial. One such term is “premium.” In this article, we will delve into the concept of premiums in insurance, exploring what they are, how they are calculated, and the factors that influence them.
What Are Premiums?
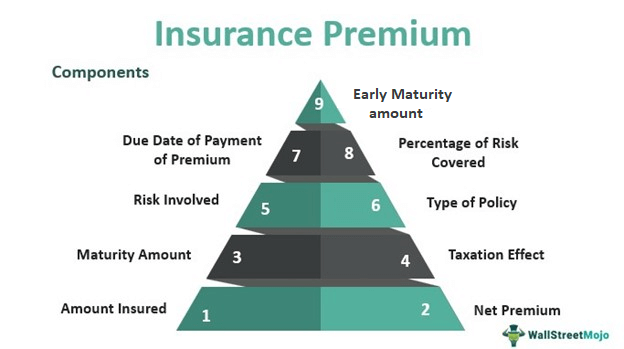
In the realm of insurance, premiums refer to the amount of money policyholders pay to insurance companies in exchange for coverage. They are recurring payments made at regular intervals, typically monthly, quarterly, or annually. The premium amount varies based on factors such as the type of insurance, the level of coverage, the policyholder’s risk profile, and other pertinent considerations.
Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums
Several factors come into play when determining insurance premiums. Let’s take a closer look at some key influencers:
Age and Gender
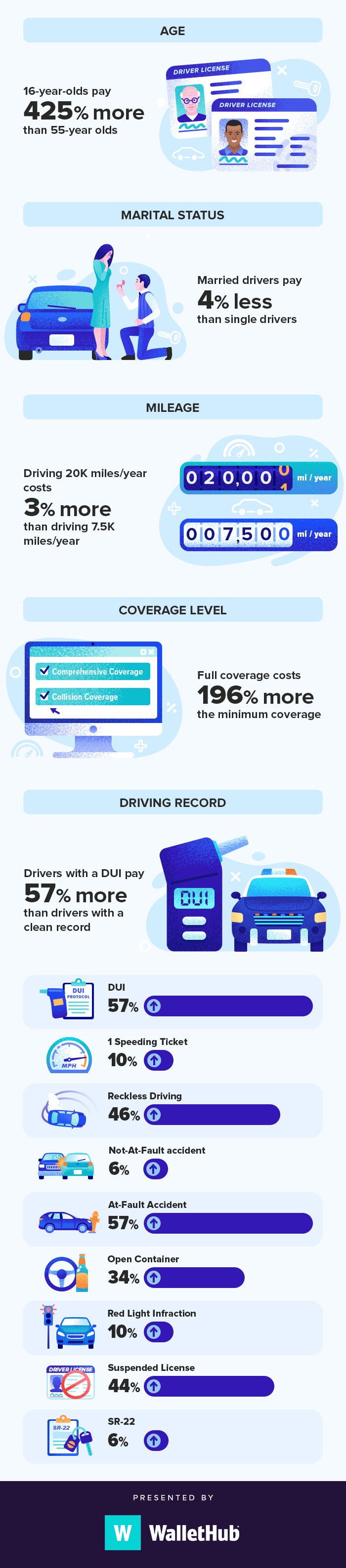
Age and gender are crucial factors in insurance premium calculations. Insurance providers analyze historical data to assess risk levels associated with different age groups and genders. For example, younger individuals may pay higher premiums for life insurance due to a perceived higher risk of mortality.
Health and Lifestyle
The health and lifestyle of the insured individual also impact premiums. Insurance companies may evaluate medical conditions, body mass index (BMI), smoking habits, and other lifestyle factors that could potentially affect the likelihood of claims being made.
Occupation and Industry
Certain occupations and industries entail higher risks, and insurance premiums may reflect this. For instance, individuals working in hazardous occupations or industries with a higher rate of accidents may face increased premiums for workers’ compensation or disability insurance.
Coverage Amount and Policy Type
The level of coverage and the type of insurance policy selected directly influence premiums. Generally, higher coverage amounts translate to higher premiums. Additionally, policies with more extensive coverage or additional features may come at a higher cost.
Types Of Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums can vary across different insurance types. Let’s explore some common examples:
- Life Insurance Premiums
Life insurance premiums are the payments made to maintain life insurance coverage. These premiums can be fixed or vary over time, depending on the type of policy chosen.
Health insurance premiums are the costs associated with maintaining health insurance coverage. These premiums can be paid by individuals or employers on behalf of their employees. The amount of the premium depends on factors such as age, health condition, coverage level, and the insurance provider.
- Auto Insurance Premiums
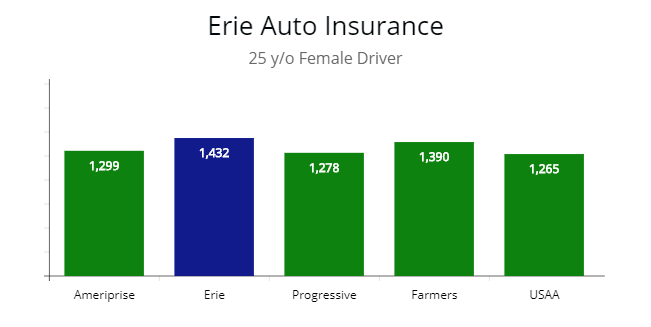
Auto insurance premiums are the payments made to insure vehicles against potential damages or accidents. The premium amount is determined by factors such as the driver’s age, driving record, type of vehicle, coverage options, and the location where the vehicle is primarily driven.
- Homeowners Insurance Premiums
Homeowners insurance premiums are the fees paid to protect homes and properties against various risks, such as fire, theft, and natural disasters. The premium amount is influenced by factors like the location of the property, its value, the policy coverage, and the deductible chosen.
- How Premiums are Calculated
Insurance premiums are calculated through a meticulous process that takes several factors into account. The following steps are generally involved in determining the premium amount:
- Underwriting Process
Insurance companies conduct underwriting to evaluate the risks associated with providing coverage. Underwriters assess factors such as the applicant’s age, health, occupation, lifestyle, and claims history to determine the level of risk involved.
- Risk Assessment
Based on the information gathered during the underwriting process, insurance providers analyze the potential risks associated with insuring an individual or asset. This risk assessment helps in determining the premium amount.
Actuaries play a vital role in the insurance industry by using statistical models and mathematical calculations to estimate future risks and determine appropriate premium rates. They consider factors such as historical data, mortality rates, accident statistics, and economic trends to arrive at the premium amount.
Premium Payment Options
Insurance companies provide various payment options for policyholders to pay their premiums. Common methods include:
- Monthly installments: Paying the premium in equal monthly installments.
- Quarterly or semi-annual payments: Paying the premium every three or six months.
- Annual payment: Paying the full premium amount upfront for the entire coverage period.
The choice of payment option depends on the policyholder’s preference and financial capabilities.
Ways To Reduce Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums can sometimes be quite expensive. However, there are strategies to potentially lower them. Consider the following methods:
- Comparison Shopping
Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers to compare premiums and coverage options. This allows you to find the most cost-effective policy that meets your needs.
- Increasing Deductibles
Opting for higher deductibles can lower your premium amount. However, be sure you can comfortably afford the deductible in the event of a claim.
- Bundling Policies
Some insurance companies offer discounts for bundling multiple policies, such as combining auto and homeowners insurance. This can result in significant savings.
- Maintaining a Good Credit Score
A good credit score can positively impact insurance premiums. Insurance companies often consider credit history when calculating premiums, as it can be an indicator of financial responsibility.
What Is The Difference Between A Premium And A Deductible?
A premium is the recurring payment made to maintain insurance coverage while a deductible is the amount the policyholder must pay out of pocket before the insurance company begins to cover the costs. Premiums are paid regularly, whereas deductibles are paid when a claim is filed.
Conclusion
Understanding insurance premiums is essential for navigating the insurance landscape effectively. Premiums represent the cost of obtaining coverage and are influenced by various factors specific to each insurance type. By comprehending how premiums are calculated and exploring ways to potentially reduce them, individuals can make informed decisions when purchasing insurance policies.